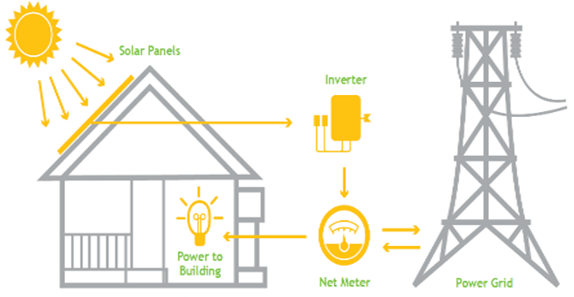
SOLAR Energy SYSTEM TERMINOLOGIES
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Panel :
Solar energy begins with the sun. Solar panels (also known as “PV panels”) are used to convert light from the sun, which is composed of particles of energy called “photons”, into electricity that can be used to power electrical loads.
Inverter:
A solar inverter works by taking in the variable direct current, or ‘DC’ output, from your solar panels and transforming it into alternating 120V/240V current, or ‘AC’ output. The appliances in your home run on AC, not DC, which is why the solar inverter must change the DC output that is collected by your solar panels.



Photovoltaic (PV):
The phenomenon of converting light to electric power. Photo = light, Volt = electricity. It is this effect that makes solar panels useful, as it is how the cells within the panel convert sunlight to electrical energy. The photovoltaic effect was first discovered in 1839 by Edmond Becquerel. When doing experiments involving wet cells, he noted that the voltage of the cell increased when its silver plates were exposed to the sunlight.
Battery:
The batteries for your solar panels is just like the battery in your phone, it can store power to use at a later time. Solar batteries will retain the surplus power your solar panels produce, when the sun goes down. There are times when your panels may produce more power than what your home actually uses. Where does that power go? Either you store in a battery or send it to grid through Net Metering.

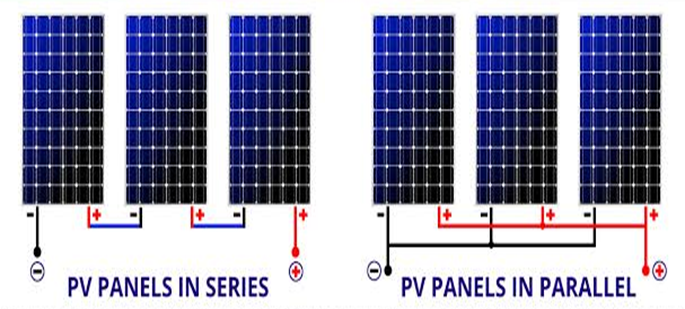
If more than one solar panels are arranged in series or parallel structure, it is termed as solar array.
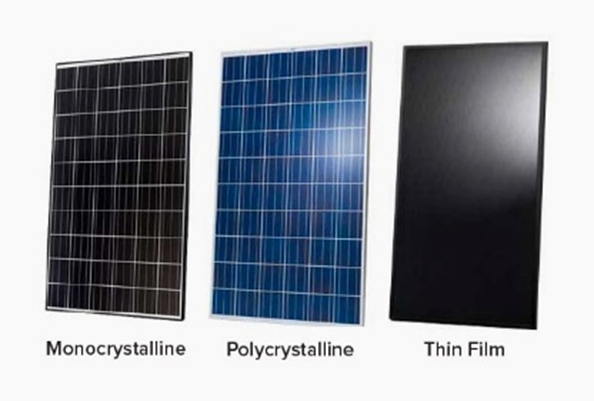
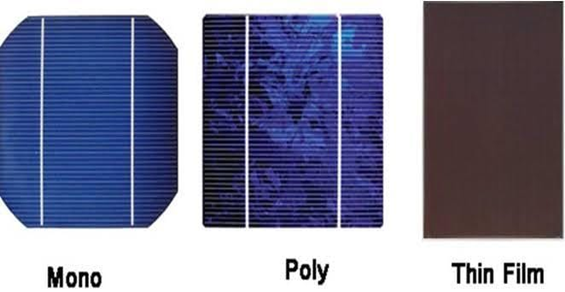
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon.It is a form of photoelectric cell, defined as a device whose electrical characteristics, such as current, voltage, or resistance, vary when exposed to light. Individual solar cell devices are often the electrical building blocks of photovoltaic modules, known colloquially as solar panels.


Direct Current, the type of power produced by photovoltaic panels and by storage batteries. The current flows in one direction and polarity is fixed, defined as positive (+) and negative (-).
Solar Charge Controller
To protect battery life the DC current is not directly fed to the battery it is sent thru the charge controller. It prevents the battery from overcharging by regulating the voltage and current coming from solar panel.
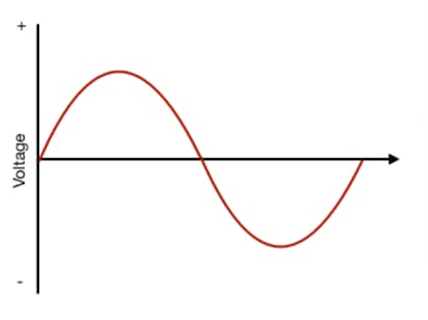
Alternating Current, the standard form of electrical current supplied by the utility grid and by most fuel-powered generators. The polarity (and therefore the direction of current) alternates. In most homes and businesses the AC is used. It is in single-phase and three-phase.
Multimeter:
A multimeter is a measuring instrument that can measure multiple electrical properties. A typical multimeter can measure voltage, resistance, and current, in which case it is also known as a volt-ohm-milliammeter (VOM), as the unit is equipped with voltmeter, ammeter, and ohmmeter functionality, or volt-ohmmeter for short. Some feature the measurement of additional properties such as temperature and capacitance.

Net Metering:
Net metering (or net energy metering, NEM) is an electricity billing mechanism that allows consumers who generate some or all of their own electricity to use that electricity anytime, instead of when it is generated. This is particularly important with renewable energy sources like wind and solar